Unveiling the Secrets of Tardigrade Resilience
Microscopic marvels of survival, tardigrades have captured the imagination of scientists and nature enthusiasts alike. These tiny creatures, also known as water bears or moss piglets, possess an extraordinary ability to withstand extreme conditions that would be fatal to most other organisms. From the depths of the ocean to the vacuum of space, tardigrades have demonstrated an unparalleled resilience that continues to baffle researchers and inspire new frontiers in scientific discovery.
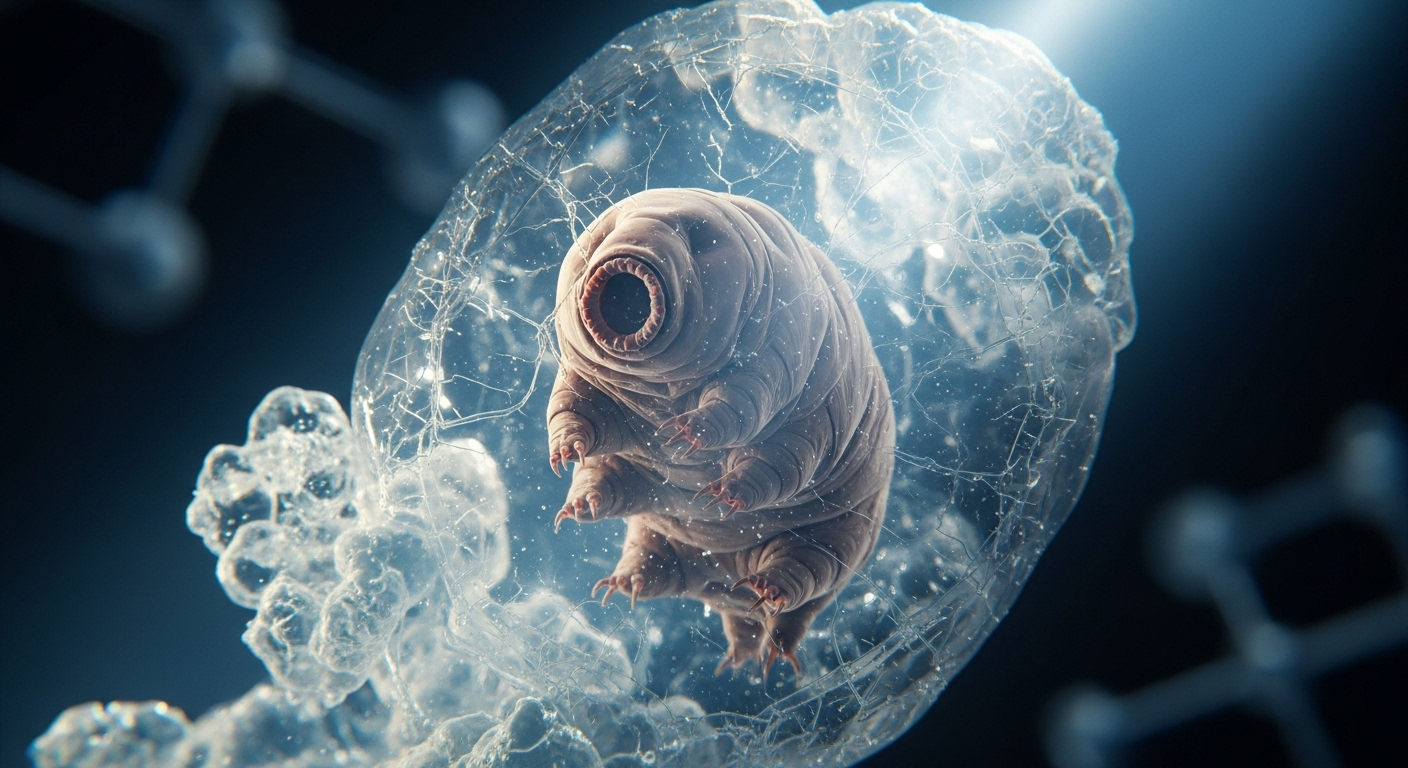
The Fascinating World of Tardigrades
Tardigrades, belonging to the phylum Tardigrada, are microscopic animals that have been around for over 500 million years. These eight-legged creatures measure between 0.3 to 0.5 millimeters in length and can be found in various environments worldwide, from mossy forests to deep-sea sediments. Despite their diminutive size, tardigrades have become renowned for their incredible resilience and ability to survive in conditions that would be lethal to most other organisms.
Unraveling the Secrets of Tardigrade Survival
The key to tardigrade survival lies in their ability to enter a state of cryptobiosis, a form of suspended animation where their metabolism slows down to near-zero levels. When faced with extreme conditions, tardigrades can curl up into a dehydrated ball called a tun, reducing their water content to as little as 1% of their normal state. In this form, they can withstand temperatures ranging from -272°C to 150°C, pressures six times greater than those found in the deepest ocean trenches, and even the vacuum of space.
Tardigrade Superpowers: More Than Just Survival
Beyond their ability to withstand extreme conditions, tardigrades possess a range of other remarkable abilities. They can survive radiation levels thousands of times higher than what would be lethal to humans, thanks to a unique protein called Dsup (Damage Suppressor) that protects their DNA. Additionally, tardigrades can go without food or water for up to 30 years and still resume normal biological functions when rehydrated.
Implications for Science and Technology
The extraordinary resilience of tardigrades has far-reaching implications for various fields of science and technology. Researchers are studying tardigrade proteins and genes to develop new methods for preserving vaccines, medicines, and even human organs for transplantation. The space industry is particularly interested in tardigrade biology, as understanding their survival mechanisms could lead to better protection for astronauts and equipment during long-term space missions.
Tardigrades in Popular Culture and Education
The unique characteristics of tardigrades have not only captured the attention of scientists but have also made their way into popular culture. These tiny creatures have been featured in various documentaries, science fiction stories, and even video games. Educational institutions are using tardigrades as a fascinating subject to engage students in biology and environmental science, highlighting the importance of biodiversity and the wonders of adaptation in the natural world.
Challenges in Tardigrade Research
Despite their remarkable abilities, studying tardigrades presents several challenges. Their microscopic size makes them difficult to observe and manipulate, requiring specialized equipment and techniques. Moreover, the vast diversity within the tardigrade phylum – with over 1,000 known species – means that findings from one species may not apply to all. Researchers are constantly developing new methods to overcome these obstacles and unlock more secrets of tardigrade biology.
The Future of Tardigrade Studies
As technology advances, so does our ability to study these fascinating creatures. Emerging fields such as genomics and proteomics are providing new insights into the molecular basis of tardigrade resilience. Scientists are also exploring the potential applications of tardigrade-inspired technologies in fields ranging from medicine to materials science. The future of tardigrade research holds exciting possibilities for scientific breakthroughs and innovative solutions to some of humanity’s most pressing challenges.
Tardigrades and Environmental Conservation
The study of tardigrades also highlights the importance of preserving biodiversity and protecting even the smallest organisms in our ecosystems. These microscopic animals play crucial roles in various habitats, from soil ecosystems to aquatic environments. Understanding their biology and ecology can provide valuable insights into the health of our planet and the impacts of climate change on microfauna.
Tiny Giants of the Natural World
Tardigrades, with their extraordinary abilities and potential applications, stand as a testament to the wonders of evolution and the incredible diversity of life on Earth. As we continue to unravel the secrets of these microscopic marvels, we not only expand our scientific knowledge but also gain a deeper appreciation for the resilience and adaptability of life in all its forms. The study of tardigrades reminds us that sometimes the most profound insights come from the smallest of creatures, challenging us to look beyond the obvious and explore the hidden wonders of the natural world.





